3 Which of the Following Is Not a Differential Stain
Using the Gram stain the age of the culture may influence the results of the stain. Capnocytophaga canimorsus is a fastidious slow-growing Gram-negative rod of the genus Capnocytophaga.

Multiple Choice Questions On Gram Staining
Other differential staining methods include the endospore stain to identify endospore-forming bacteria the acid-fast stain to discriminate.
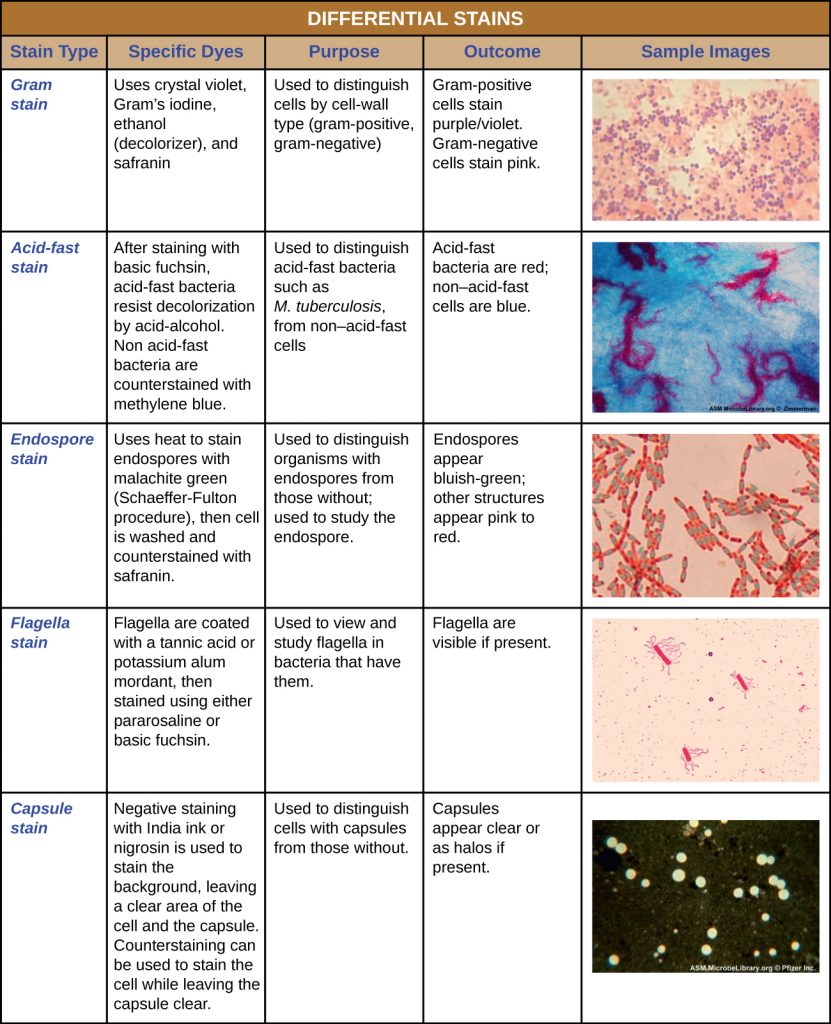
. Stains for connective tissues are among the most. Gram Stain The previous lab introduced simple staining techniques that enable microbiologists to observe the morphological characteristics of bacteria. A differential stain consists of two or more dyes and is used in the procedure to identify bacteria.
The combination of polychrome methylene blue and eosin stains has selective staining properties. Strong and diffuse block positive p16 results support a categorization of precancerous disease If there is a professional disagreement in histologic interpretation when the differential diagnosis includes a. For example members of the genusAcinetobacter are gram-negative cocci that are resistant to the decolorization step of the Gram stainAcinetobacter spp.
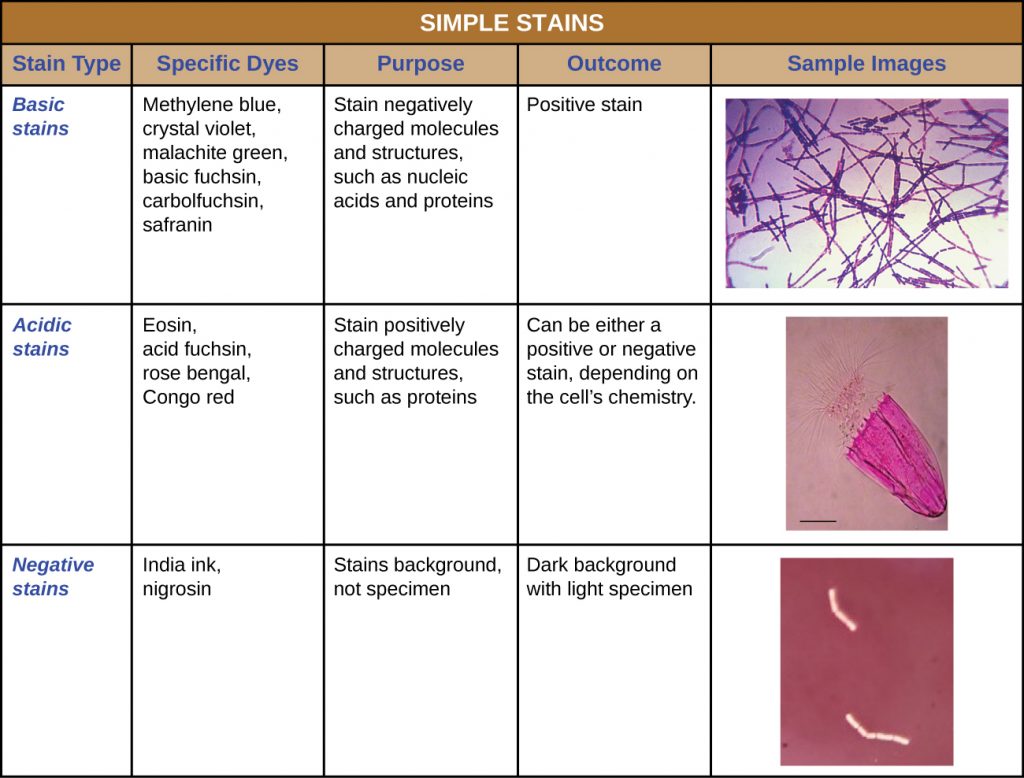
Therefore making an accurate. Gram-positive microorganisms stain purple. Although simple stains are useful they do not reveal details about the bacteria other.
Typical histological findings of sarcoidosis are discrete well-formed. One of the most commonly used differential stains is the gram stain. Can assess shape Can.
Canimorsus generally has low virulence in healthy individuals. Escherichia coli is gram. Tinea corporis can often be diagnosed on the basis of a positive potassium.
The result obtained is. It is a commensal bacterium in the normal gingival flora of canine and feline species but can cause illness in humans. Can assess shape Can assess cellular arrangement Can assess size Can assess motility Can assess whether Gram-negative or positive.
The Gram stain is an example of a differential stain. White cells can be counted manually in specially designed chambers Neubauer or with automated counters. The differential staining allows one to identify the types of white blood cells on the.
Transmission may occur through bites licks or even close proximity with animals. Negative stain Simple stain Differential stain Gram stain. The diagnosis of sarcoidosis can be made by fulfilling the following criteria.
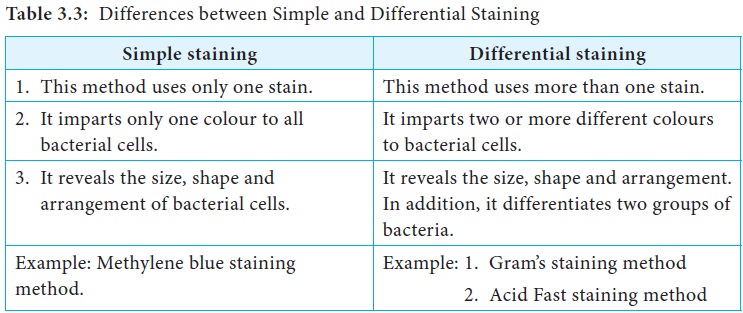
Differential staining methods which typically require more than one stain and several steps are referred to as such because they permit the differentiation of cell types or cell structures. The best combination was with a welding time of 35 s devised to 05 s and 3 s and welding pressure 25 and 4 MPa respectively. HE is the mainstay of diagnostic histopathology.
Gram Stain and Acid-fast Stain II. Identify a dye that results in a negative stain. The differential count may be performed after the wbc blood count has been determined by the automated 3 part differential and may be used as a double check on the white blood cell count.
Although this stain can elucidate most histological features a variety of special stains are often useful for identifying features that are otherwise not apparent in liver tissue. A common bacterium that causes food poisoning Staphylococcus aureus is gram-positive. The simplest test is the WBC count and differential.
The decision as to which stains should be routinely used is largely a matter of personal preference. Identify the benefits of using a hanging drop mount. If the differential diagnosis is between precancer IN 2 or IN 3 and either a mimic of precancer or a low grade non HPV associated lesion.
Some bacteria do not stain as expected with the Gram stain. Often appear gram-positive after a well prepared. Before staining and observing a microbe under a microscope a smear must be prepared.
Alcohol India ink Eosin Cyanosin. 1 a compatible clinical andor radiological abnormality 2 histological confirmation of noncaseating granulomas and 3 exclusion of other diseases capable of presenting similar histological and clinical manifestations. To determine the differential a drop of blood is thinly spread over a glass slide air dried and stained with a.
The most important of these is the Gram stain. The lesion does not regress with the application of silver nitrate and surgical excision is often recommended due to the possibility of an underlying OMD remnant such as a Meckel diverticulum fistula sinus tract OMD cyst or obliterated duct fibrous cord 2369. Although most annular lesions will be typical of a dermatophytosis physicians must consider other possible diagnoses.
The clinical outcomes of umbilical polyps vary from trivial to severe. The latter are widely used offering the advantage of higher accuracy and speed over manual techniques. Specialized stains detect specific structures of cells such as flagella and endospores.
Gram-negative microorganisms stain pink. The goal of smear preparation is to place an appropriate concentration of cells on a slide and then. 3 - 6 Preparation of a Bacterial Smear for Staining.
2 4 Staining Microscopic Specimens Microbiology Canadian Edition
Differential Staining Method Procedure Principle Importance

2 4 Staining Microscopic Specimens Microbiology Canadian Edition
No comments for "3 Which of the Following Is Not a Differential Stain"
Post a Comment